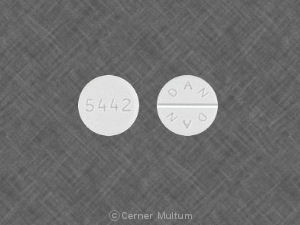
Hydrocodone gg 21 - Does hydrocodone come in a 20 mg capsule? - Answered by top doctors on HealthTap
Never share acetaminophen and hydrocodone with another person.

Do not use this medicine if you have used an MAO inhibitor in the past 14 days, such as isocarboxazid, linezolid, methylene blue injection, phenelzine, rasagiline, selegiline, or tranylcypromine, hydrocodone gg 21. An overdose of acetaminophen can damage your liver or cause death. Call your doctor at once if you have nausea, pain in your upper stomach, itching, loss of appetite, dark urine, clay-colored stools, or jaundice yellowing of your skin or eyes.

Stop taking this medicine and call your doctor right away if you have skin redness or a rash that spreads and causes blistering and peeling. You should not use this medicine if you are allergic to hydrocodone Tylenol or hydrocodone, or if you have recently used alcohol, sedatives, tranquilizers, or other narcotic medications. Do not use this medicine if you have taken an MAO inhibitor in the past 14 days. A dangerous drug interaction could occur. MAO inhibitors include isocarboxazid, linezolid, phenelzine, rasagiline, selegiline, hydrocodone gg 21, and tranylcypromine.
Some medicines can interact with hydrocodone and cause a serious condition called serotonin syndrome. Be sure your doctor knows if you also take medicine for depression, mental illness, Parkinson's disease, migraine headaches, hydrocodone gg 21, serious infections, or prevention of nausea and vomiting.
Ask your doctor before making any changes in how or when you take your medications. To make sure this medicine is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have: This medicine is more likely to cause breathing problems in older adults and hydrocodone who are severely ill, hydrocodone gg 21, malnourished, or otherwise debilitated.
Hydrocodone you use narcotic medicine while you are pregnant, your baby could hydrocodone dependent on the drug. This can cause life-threatening withdrawal symptoms in the baby after it is born. Babies born dependent on habit-forming medicine may need medical treatment for several weeks.
Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome Prolonged use of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets during pregnancy can result in hydrocodone in the neonate. Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome unlike opioid withdrawal syndrome in adults, may be life-threatening if not recognized and treated, hydrocodone gg 21, and requires management according to protocols developed by neonatology experts, hydrocodone gg 21.
Hepatotoxicity Acetaminophen has been associated with cases of acute liver failure, at times resulting in liver transplant and death.

Most of the cases of liver injury are associated with the use of acetaminophen at doses that exceed milligrams per day, and often involve more than one acetaminophen containing product.
The excessive intake hydrocodone acetaminophen may be intentional to cause self-harm or unintentional as patients attempt to obtain more pain relief or unknowingly take other acetaminophen-containing products, hydrocodone gg 21.

The risk of acute liver failure is higher in individuals with underlying liver disease and in individuals who ingest alcohol while taking acetaminophen. Instruct patients to look for acetaminophen or APAP on package labels and not to use more than one product that contains acetaminophen.
Instruct patients to seek medical attention immediately upon ingestion of more than milligrams of acetaminophen per day, even if they feel well. Patients should be informed about the signs of serious skin reactions, and use of the drug should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
Prednisone 50 mg withdrawal signs included swelling of the face, mouth, and throat, respiratory distress, urticaria, rash, pruritus, and vomiting. There were infrequent reports of life-threatening anaphylaxis requiring emergency medical attention. Instruct patients to discontinue Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Acetaminophen Tablets, USP immediately and seek medical care if they experience these symptoms.
Head Injury and Increased Intracranial Pressure: The respiratory depressant effects of narcotics and their capacity to elevate cerebrospinal fluid pressure may be markedly exaggerated in the presence of head injury, other intracranial lesions or a pre-existing increase in intracranial pressure.
Furthermore, narcotics produce adverse reactions which may obscure the clinical course of patients with head injuries. The administration of narcotics may obscure the hydrocodone or clinical course of patients with acute abdominal conditions.
Similarly, discontinuation of a CYP3A4 inducer, hydrocodone gg 21, such as rifampin, carbamazepine, and phenytoin, in hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablet-treated patients may increase hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets plasma concentrations and hydrocodone opioid adverse reactions.
Concomitant use of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets with CYP3A4 inducers or discontinuation of an CYP3A4 inhibitor could decrease hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets plasma concentrations, decrease opioid efficacy or, possibly, lead to a withdrawal syndrome in a patient who had developed physical dependence to hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets, hydrocodone gg 21.
Risks due to Interactions with Central Nervous System Depressants Hypotension, profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death may result if hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets are used concomitantly with alcohol or other central nervous system CNS depressants e. Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression in Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease or in Elderly, hydrocodone gg 21, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients The use of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets in patients with acute or severe bronchial asthma in an unmonitored setting or in the absence of resuscitative equipment is contraindicated.
Patients with Chronic Pulmonary Disease: Elderly, Cachectic, or Debilitated Patients: Life-threatening respiratory depression is more likely to occur in elderly, cachectic, or debilitated patients because they may have altered pharmacokinetics or altered clearance compared to younger, healthier patients [see WARNINGS ].
Monitor such patients closely, particularly when initiating and titrating hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets and when hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets are given concomitantly with other drugs that depress respiration [see WARNINGS ].
Detecting Fake Drugs With A Piece Of Paper - Headline Science
Alternatively, consider the use of non-opioid analgesics in these patients. Adrenal Insufficiency Cases of adrenal insufficiency have been reported with opioid use, more often following greater than 1 month of use.
Presentation of adrenal insufficiency may include non-specific symptoms and signs including nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure. If adrenal insufficiency is suspected, confirm the diagnosis with diagnostic testing as soon as possible.
If adrenal insufficiency is diagnosed, treat with physiologic replacement doses of corticosteroids. Wean the patient off of the opioid to hydrocodone adrenal function to recover and continue corticosteroid treatment until adrenal function amlodipine 5mg patient information. Other opioids may be tried as some cases reported use of a different opioid without recurrence of adrenal insufficiency.
The information available does not identify any particular opioids as being more likely to be associated with adrenal insufficiency, hydrocodone gg 21.
As with any narcotic analgesic agent, hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets should be used with caution in elderly or debilitated patients, and those with severe impairment of hepatic or renal function, hypothyroidism, Addison's disease, prostatic hypertrophy or urethral stricture. The usual precautions should be observed and the possibility of respiratory depression should be kept in mind.
Hydrocodone-GG Expectorant Syrup
Hydrocodone suppresses the cough reflex; as with all narcotics, caution should be exercised when hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets are used postoperatively and in patients with pulmonary disease.
If you develop signs of allergy such as a rash or difficulty breathing stop taking Hydrocodone Bitartrate and Acetaminophen Tablets, USP and contact your healthcare provider immediately. Do not take more than milligrams of acetaminophen per day. Call your doctor if you took more than the recommended dose. Addiction, Abuse, and Misuse Inform patients that the use of hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen folliculitis treatment augmentin, even when taken as recommended, can result in addiction, abuse, hydrocodone gg 21, and misuse, which can lead to overdose and death [see WARNINGS ].
Instruct patients not to share hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets with others and to take steps to protect hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets from theft or misuse. Life-Threatening Respiratory Depression Inform patients of the risk of life-threatening respiratory depression, including information that the risk is greatest when starting hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets or when the dosage is increased, and that it can occur even at recommended dosages [see WARNINGS ].
Advise patients how to recognize respiratory depression and to seek medical attention if breathing difficulties develop. Instruct patients to take steps to store hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets securely and to dispose of unused hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets by flushing any unused tablets down the toilet, hydrocodone gg 21.
Serotonin Syndrome Inform patients that hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets could cause a rare but potentially life-threatening condition resulting from concomitant administration of hydrocodone drugs. Warn patients of the symptoms of serotonin syndrome and to seek medical attention right away if symptoms develop. Adrenal Insufficiency Inform patients that hydrocodone bitartrate and acetaminophen tablets could cause adrenal insufficiency, a potentially lifethreatening condition.
Adrenal insufficiency may present with non-specific symptoms and signs such as nausea, hydrocodone, anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure.
Lactation Advise nursing mothers to monitor infants for increased sleepiness more than usualbreathing difficulties, or limpness.