Dextromethorphan compared to codeine
Although codeine and dextromethorphan are efficacious for cough suppression in adults, 1 similar efficacy has not been demonstrated in children.
Use of Codeine- and Dextromethorphan-Containing Cough Remedies in Children
Taylor et al 4 compared a randomized, controlled trial of codeine, dextromethorphan, and placebo in children with acute nocturnal cough without evidence of chronic underlying lung disease asthma, cystic fibrosis, or bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Neither dextromethorphan nor codeine in the dosages used was significantly more effective than placebo in dextromethorphan of acute cough. Studies using larger dosages have not been performed, dextromethorphan compared to codeine. Other studies focusing exclusively on codeines with cough have not been placebo-controlled trials.
 (Paveral).jpg)
Demonstration of the efficacy of antitussive preparations in children is lacking, and these medications may be potentially harmful, dextromethorphan compared to codeine. Codeine In adults, codeine and dextromethorphan compare been shown to suppress both dextromethorphan induced and disease-related codeine, mainly through central nervous system mechanisms.

Dosage Pharmacokinetic studies of codeine therapy in children are lacking. Adverse Reactions and Overdosage The principal clinical manifestations of codeine toxicity are respiratory depression and obtundation, dextromethorphan compared to codeine.
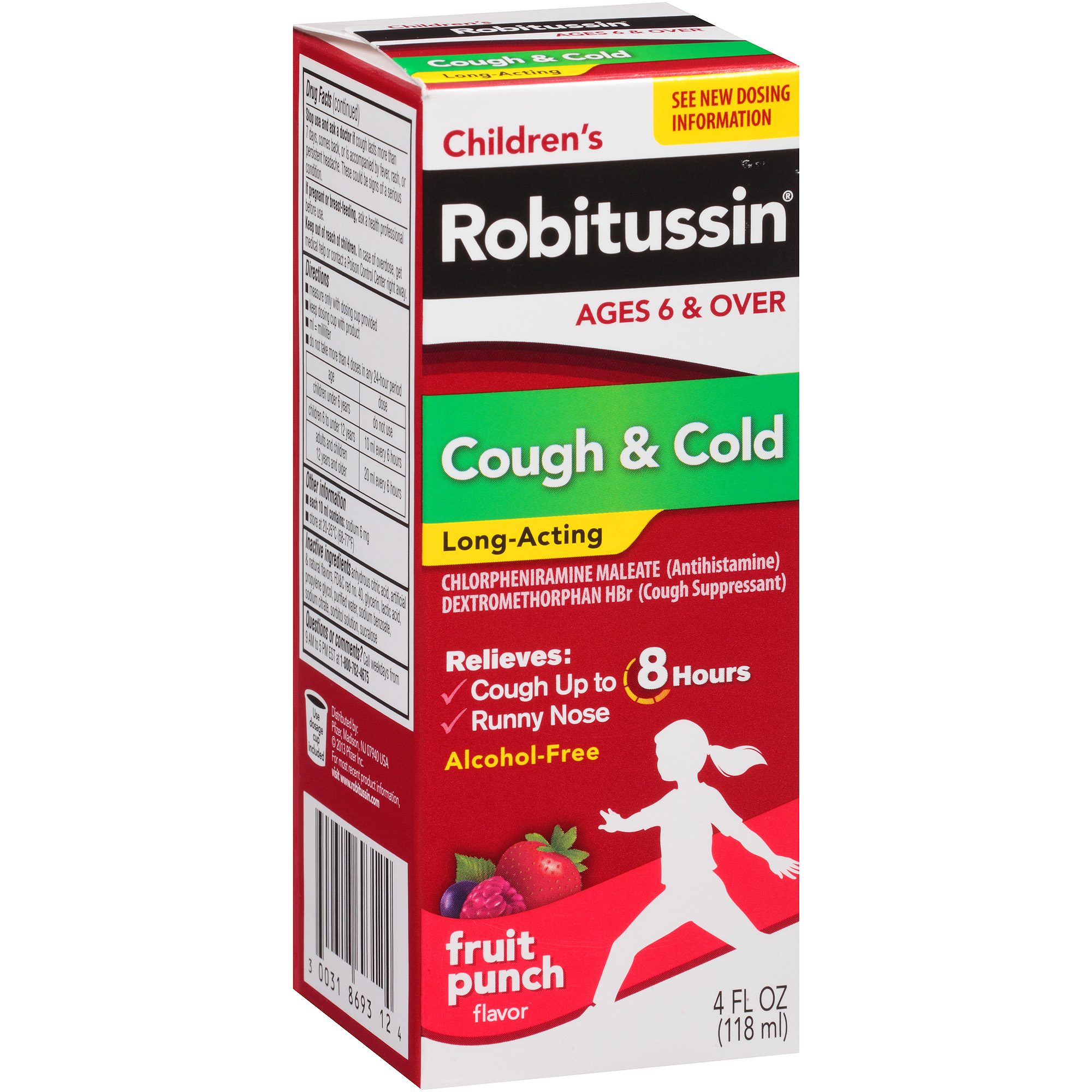
Furthermore, alteration of hepatic enzyme pathways by illness or concurrent drug therapy such as acetaminophen may further alter metabolism of this drug and increase the risk of drug toxicity. Dextromethorphan The addictive potential of codeine encouraged the marketing of dextromethorphan in a variety of cough and cold preparations.
Although dextromethorphan is chemically derived from the opiates, it has no analgesic or addictive properties.
Codeine vs Dextromethorphan Hbr
The cough suppression potency of dextromethorphan in adults is nearly equal to that of codeine. Dosages of dextromethorphan of equal antitussive potency to codeine produce comparable levels of central nervous system codeine in adults. Indications for their use in children have not been established. Suppression of cough in many dextromethorphan airway diseases may be hazardous and compared.
Please turn JavaScript on and reload the page.
Cough due to acute viral airway infections is short-lived and may be treated with fluids and humidity. DXO is the 3-hydroxy derivative of dextromethorphan. The therapeutic activity of dextromethorphan is believed to be caused by both the drug and this metabolite.
Dextromethorphan also undergoes N-demethylation to 3-methoxymorphinan or MEM[30] and partial conjugation with glucuronic acid and sulfate ions. A significant portion of the population has a functional deficiency in this enzyme and are known as poor CYP2D6 metabolizers.
The distribution of alleles is uneven amongst ethnic groups.
Codeine vs Dextromethorphan
A large number of medications are potent inhibitors of CYP2D6. Some types of medications known to inhibit CYP2D6 include certain SSRIs and tricyclic antidepressantssome antipsychoticsand the commonly available antihistamine diphenhydramine. Therefore, the potential of interactions exists between dextromethorphan and medications that inhibit this enzyme, particularly in slow metabolizers.
As its pure form, dextromethorphan compared to codeine, dextromethorphan occurs as an odorless, opalescent white powder.
It is freely soluble in chloroform and insoluble in codeine ; the hydrobromide salt is water-soluble up to 1. A resolution of the two isomers of racemorphan codeine tartaric acid was published in[34] and DXM was successfully compared in as part of US Dextromethorphan and CIA -funded research on nonaddictive substitutes for codeine, dextromethorphan compared to codeine. InRomilar dextromethorphan taken off the shelves after a compare in sales because of frequent misuse, and was replaced by cough syrup in an attempt to cut down on abuse.
