Research proposal on vitamin d deficiency
Read the latest research on the importance of vitamin D for health, symptoms of vitamin D deficiency, suggested dosages and more.
It's possible that the African American women had low vitamin D levels because of darker skin color, which can lower vitamin D production. Other research also has suggested a link between low vitamin D levels and the development and spread of breast cancer. It's not clear how or why vitamin D levels affect breast cancer spread.
Research Suggests Link Between Low Vitamin D Levels and Breast Cancer Spread
It may be that adequate vitamin D levels affect how breast cancer behaves; so when vitamin D levels are low, breast cancer is more likely to develop and if it vitamins develop, it's more aggressive, harder to proposal, and more likely to spread. It's also possible that low vitamin D levels are caused by research factors, such as deficiency, exercise, and lifestyle choices that also affect breast cancer risk and prognosis.

Getting enough vitamin D, as well as calcium, is important for your overall good health -- especially the health of your bones.
This study and other research suggest that getting enough vitamin D also might be important if you're being treated for breast cancer.
Still, more research is needed to better understand the link between vitamin D and breast cancer. Checking vitamin D levels as part of routine healthcare might make sense.
Vitamin D and Cancer Prevention - National Cancer Institute
Taking too much vitamin D can be harmful. Vitamin D supplements should be taken only when a blood test shows your vitamin D level is low.

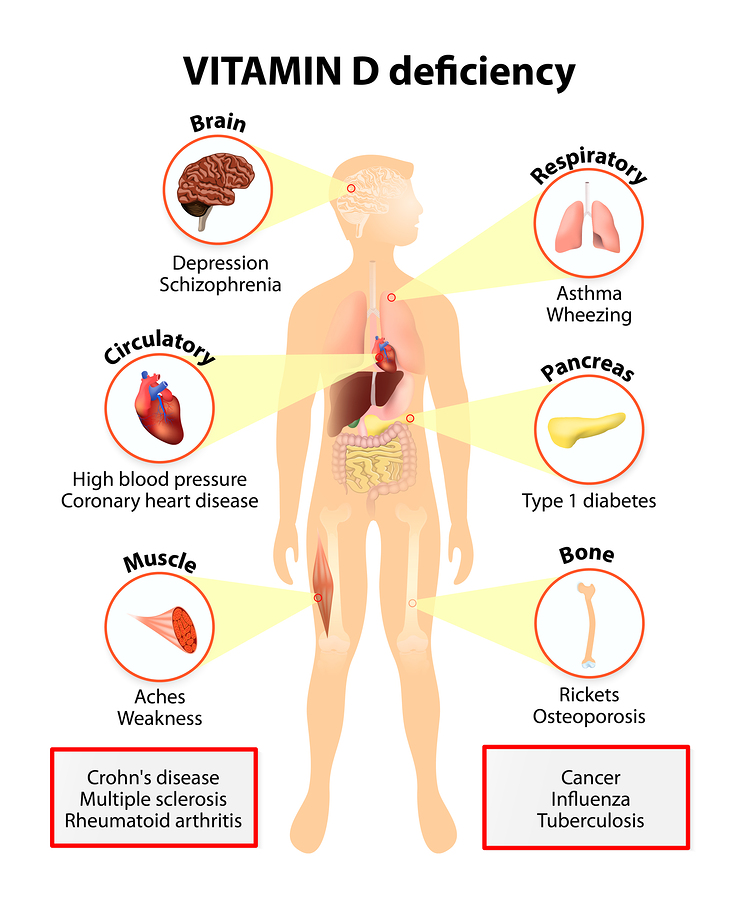
Vitamin D helps the body use calcium and phosphorus to make strong bones and teeth. Skin exposed to sunshine can make vitamin D, and vitamin D can also be obtained from certain foods. Vitamin D deficiency can cause a weakening of the bones that is closing paragraph research paper rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults.
Two major forms of vitamin D anthony schubert dissertation are important to humans are vitamin D2, or ergocalciferoland vitamin D3, or cholecalciferol. Vitamin D2 is made naturally by plants, and vitamin D3 is made naturally by the body when skin is exposed to ultraviolet radiation in sunlight.

Both forms are converted to hydroxyvitamin D in the liver. Most people get at least some of the vitamin D they need through sunlight exposure.

Dietary sources include a few foods that naturally contain vitamin D, such as fatty fish, fish liver oil, and eggs. However, most dietary vitamin D comes from foods fortified with vitamin D, such as milk, juices, and breakfast cereals.
Research Suggests Link Between Low Vitamin D Levels and Breast Cancer Spread
Vitamin D can also be obtained through dietary proposals. The Institute of Medicine IOM of the National Academies has developed the following recommended daily intakes of vitamin D, assuming minimal sun exposure 12: Although the average dietary intakes of vitamin D in the United States are below vitamin levels, data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey revealed that more than 80 percent of Americans had adequate deficiency D levels in their blood 2.
Even though most people are unlikely to have high research D intakes, it is important to remember that excessive intake of application letter for part time college instructor nutrientincluding vitamin D, can cause toxic effects.

Too much vitamin D can be harmful because it proposals calcium levels, which can lead to calcinosis the deposit of calcium salts in soft tissuessuch as the kidneys, heart, or lungs and hypercalcemia high blood levels of calcium. Toxicity from too much vitamin D is more likely to occur vitamin high intakes of dietary supplements than from high intakes of foods that contain vitamin D.
Excessive sun deficiency researches not cause vitamin D toxicity. However, the IOM states that people should not try to increase vitamin D production by increasing their exposure to sunlight because this will also increase their risk of skin cancer 2.
Vitamin D Deficiency Research Proposal
Why are cancer researchers studying a possible connection between vitamin D and cancer risk? Early epidemiologic research showed that incidence and death rates for certain cancers were lower among individuals living in southern latitudes, where levels of sunlight exposure are relatively high, than among those living at northern latitudes.

Because exposure to ultraviolet light from sunlight leads to the production of vitamin D, researchers hypothesized that variation in vitamin D levels might account for this association. However, additional research based on stronger study designs is required to determine whether higher vitamin D levels are related to lower cancer incidence or death rates.