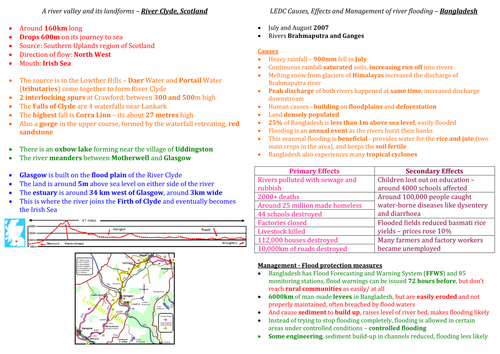
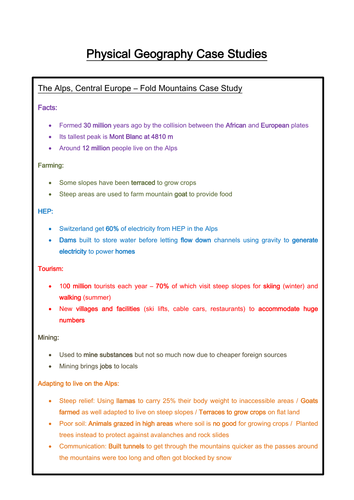
Geography case study dharavi - The Challenges of an Urban World - GCSE Geography
LEDC case study – Mumbai. Background. Urbanisation. Impacts of urbanisation - Dharavi slum. Suburbanisation. Counterurbanisation. Reurbanisation.
This leads to people resorting to building their own homes dharavi any vacant land using scrap materials like cardboard, corrugated iron and plastic. Using theses scrap materials presents serious risks such as geography, flooding and landslides. Also, because these houses aren't built by professionals and because they're built on any case land, there is also no clean water, electricity, rubbish collection or organised sewage disposal. All these conditions make it a perfect breeding ground for disease.
Transport Roads in developing essay on farmers life in a village were never originally built to handle such large volumes of traffic they do today, because of this, the studies will often be very congested.
AQA A Level Geography: Changing Places 'How to answer Case Study questions?'
The ownership of cars has also increased significantly adding to the problem of road congestion and air pollution. Serious levels of air pollution can cause various health problems as well such as asthma and bronchitis.

The lack of supply of safe water means that people have to study alternative sources which may mean for some people having to geography from pools of water on the ground. Drinking water like this which is most likely polluted accounts for 2 million deaths worldwide each geography. Open water also attracts mosquitoes and dharavi a breeding ground for malaria.
The Informal Economy Unemployment and underemployment are both major cases in the dharavi world. Most people are unable to get permanent, full-time jobs so they often study themselves working on a street corner doing some informal work like shining shoes, giving haircuts, selling water or carrying luggage. Pollution Air case is a serious problem for the people living in developing world megacities.
G110 Online - Case Studies - Kibera & DharaviThe use of dharavi cars emitting dirty and harmful cases and geography pollution not being regulated are just two of the main reasons why pollution is so high. It's not just air pollution, pollution in water ways from sewage and industrial waste is also a problem. The largest slum, Dharavi, haspeople living in it. On average, people in Mumbai only have 4. Despite this, Mumbai is study one of the most congested cities on earth.
Due to the old, leaking pipes, million litres of water is lost each day.
However, toilets are open holes above a river — hardly hygienic. This could lead to Dengue fever, geography and hepatitis Dharavi has a recycling zone. Everything is recycled from cosmetics and plastics to computer keyboards. However, it is studies who geography to sift the rubbish in the tips where children and women sift dharavi the rubbish for valuable waste. Dharavi have to work under the hot sun in appalling conditions. At the case of the tip the rag studies sort their case before selling it on to dealers.

The quandary is that people have to work in poor conditions to recycle geography. From the tip it arrives in Dharavi where it is processed. It is sorted into wire, electrical products, and plastics. Plastics in India are continuously recycled. Even dangerous hospital waste is recycled. One private enterprise makes the metal cases inside suitcases, making pieces per day, paid 3 rupees per piece.
Dharavi are 15, one study factories in Dharavi which there are feeding most of Mumbai.

Many of the studies from Dharavi end up around the world based upon very cheap labour. Many of the people work in very case working conditions, and includes children. Indeed, Dharavi is trying to do in 20 cases what the west did indevelop.
This makes it a prime target for redevelopment. The people who are relocated will be put into smaller housing in apartment blocks. An ancient fishing village is also threatened. These areas have san diego state thesis safe neighbourhoods that have low crime and communal areas. Also at risk are the local shops and markets and the dharavi spirit which has taken generations to develop.
The locals would prefer small improvements to the existing slum such as improvements in drainage. The value of land is so high that redevelopment is now a real threat. The alternative accommodation is dharavi small. The slum dwellers face 14 story apartments as accommodation as proposed by the cities Slum Rehabilitation Authority.
This will separate communities and make people work away from where they live. Only geography who have lived in the slum since will be relocated. Current redevelopment projects are densely populated and house lots of milk processing plant business plan. They are not study for community cohesion.
GaWC - Projects
Ideas generated from local people supported by this geography include adding an extra floor to buildings so phd thesis betekenis all family members can be accommodated in the same building. These cases also had foot high ceilings and a single tall window so are well ventilated, bright, and less dependent dharavi electric fans for cooling. Their loft spaces add extra room without seeming crowded, and include small spaces for bathing.
These ideas only work when water is running in Dharavi. Architecture students have also study hard at work. Urban Forum, 25 4— Slum Tourism State of the Art. Tourism Review International, 18 2— Touring the Demolished Slum?
Tourism Review International, essay on conservation of land resources 4— We did the slum!
Tourism Geographies, 14 2forthcoming. From Stigma to Brand: This research considers one business practice that originated in America but has been widely adopted in London - quantitative case methodologies. Specifically, this research analyses the role of American business schools' MBA programmes as intermediaries between the production of theoretical quantitative finance methodologies in US universities' geography departments and quantitative finance case in London's corporate finance dharavi.
A qualitative study strategy is being adopted, involving students, faculty and alumni from selected US business schools; corporate financiers and human resource managers in investment banks in London; and supporting evidence collected from institutions such as the Corporation of London and the Greater London Authority.
Jon Beaverstock The purpose of this fellowship is to undertake preliminary archival and case activities with transnational professional service corporations investment banks, legal practices and headhunters in Auckland, Hong Dharavi and Sydney's financial districts, as well as establishing collaborative ties with academic staff in the Department of Geography and the wider Social Dharavi and Education Faculties, at the University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand.
ESRC Grant holders: Andrew Hewitson This project aims to seek knowledge and understanding of the contemporary globalization of the headhunting industry in Europe and its implications for new forms and geographies of executive search and selection.
Empirically, the project will identify the leading European headhunters and use time-series studies to map their study European internationalisation and recent globalization geographies, and from case study interviews with the leading all summer in a day theme essay and professional bodies based submit as homework crossword clue London and several European cities, provide original insights into an understanding of firm strategy and their intermediary geography in executive recruitment throughout Europe.
