Zoloft cyclothymic disorder - Medications to treat Cyclothymic Disorder
What Causes Cyclothymic Disorder? Many experts say cyclothymic disorder is a very mild form of bipolar disorder. No one is sure what causes cyclothymia or bipolar disorder. Genetics play a role in the development of both these disorders. People with cyclothymia are more likely to have relatives with bipolar disorder and vice versa. What Are the Treatments for Cyclothymia? Cyclothymia frequently goes undiagnosed and untreated. Most people's symptoms are mild enough that they do not seek mental health treatment.
In fact, some people resist the idea of treatment, which reduces their "up" episodes as well as "down. Feelings of depression or instability are usually what cause people with cyclothymia to seek help.
Continued No medicines are specifically approved for the treatment of cyclothymia, although mood stabilizers such as lithium or lamotrigine are sometimes recommended as a possible strategy to reduce mood fluctuations. Antidepressants such Prozac , Paxil , or Zoloft are generally not recommended unless someone develops a full major depression , which, by definition, does not occur in cyclothymic disorder.
There is also a small risk that antidepressants could trigger or worsen mania symptoms in a subgroup of vulnerable people. Antidepressants alone also are not known to improve fluctuations in mood, which are hallmark characteristics of cyclothymic disorder.
However, bipolar disorder can affect people of all ages, including children. Bipolar disorder that occurs late in life often accompanies medical and neurological problems particularly cerebrovascular disease, such as stroke. It is less likely to be associated with a family history of the disorder than earlier-onset bipolar disorder.
Gender Bipolar disorder affects both sexes equally, but there is a higher incidence of rapid cycling, mixed states, and cyclothymia in women. Early-onset bipolar disorder tends to occur more frequently in men and it is associated with a more severe condition. Men with bipolar disorder also tend to have higher rates of substance abuse drugs, alcohol than women. Family History Bipolar disorder frequently occurs within families. Family members of patients with bipolar disorder are also more likely to have other psychiatric disorders.
They include schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, anxiety disorders, ADHD, and major depression. Possible Complications Psychiatric Comorbidities Many patients with bipolar disorder often have accompanying psychiatric disorders. Patients with bipolar disorder, especially type II or cyclothymic disorder, have frequent episodes of major depression.
Because of depression, patients with bipolar disorder have an increased risk for suicide. Anxiety disorders, such as panic disorder, phobias, and post-traumatic stress disorder also commonly coexist in these patients. Patients who also suffer from an anxiety disorder are also at greater risk for suicide. Symptoms of bipolar disorder in children are often confused with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder ADHD.
Furthermore, the two conditions can coincide. Patients with bipolar disorder frequently abuse drugs and alcohol. Although drug and alcohol abuse may be a form of self-medication, substance abuse can trigger or worsen bipolar symptoms.
Behavioral and Emotional Effects A small percentage of bipolar disorder patients demonstrate heightened productivity or creativity during manic phases. More often, however, the distorted thinking and impaired judgment that are characteristic of manic episodes can lead to dangerous behavior, including: Spending money with reckless abandon, causing financial ruin in some cases Angry, paranoid, and even violent behaviors Openly promiscuous behavior Such behaviors are often followed by low self-esteem and guilt, which are experienced during the depressed phases.
During all stages of the illness, patients need to be reminded that the mood disturbance will pass and that its severity can be diminished by treatment. Prognosis Bipolar disorder can be severe and long-term, or it can be mild with infrequent episodes.
Patients with the disease may experience symptoms in very different ways. A typical patient with bipolar disorder averages 8 - 10 manic or depressive episodes over a lifetime. However, some people experience more and some fewer episodes. Medical evidence has shown that patients with bipolar disorder have higher death rates from suicide, heart problems, and death from all causes than those in the general population.
Patients who get treatment, however, experience great improvement in survival rates. In most cases of bipolar disorder, the depressive phases far outnumber manic phases, and the cycles of mania and depression are neither regular nor predictable.
Many patients experience mixed mania, or a mixed state, in which both mania and depression coexist for at least 7 days. With this phase the manic and depressive episodes alternate at least four times a year and, in severe cases, can even progress to several cycles a day.
Rapid cycling tends to occur more often in women and in those with bipolar II. Typically, rapid cycling starts in the depressive phase, and frequent and severe episodes of depression may be the hallmark of this event. This phase is difficult to treat, particularly since antidepressants can trigger the switch to mania and set up a cyclical pattern.
Differences Between Children and Adults. Research suggests that symptoms of bipolar disorder in children and adolescents differ from those of adults.
While adults with bipolar disorder usually have distinct and persistent periods of mania and depression, children with bipolar disorder fluctuate rapidly in their mood and behavior. Mania in children is characterized by irritability and belligerence whereas adults tend to experience euphoria. Children with bipolar depression are frequently angry and restless, and may have additional mood and behavioral disorders such as anxiety, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, conduct disorder, and substance abuse problems.
It is not yet clear how frequently childhood bipolar disorder persists into adulthood or if treating childhood bipolar disorder can help prevent future illness.
Symptoms Symptoms of bipolar disorder tend to fluctuate dramatically between two extremes: Sometimes a patient may have an episode in which both symptoms of mania and depression are present at the same time. Symptoms vary among patients. The type of symptoms experienced also depend on the type of bipolar disorder.
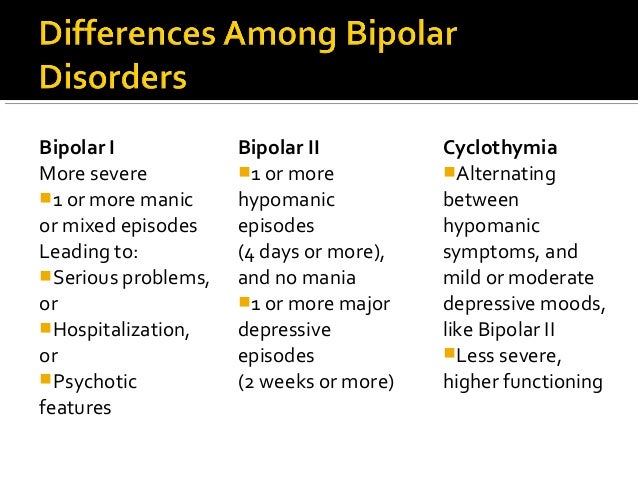
Patients with bipolar I disorder typically have severe manic episodes that alternate with shorter bouts of depressive symptoms. Patients with bipolar II disorder, experience longer periods of depression that alternate with manic episodes that are shorter in duration and less severe hypomania than those associated with bipolar I disorder.
Symptoms of Mania Symptoms associated with manic episodes include: A feeling of great happiness or well-being Irritability. Can include aggressive behavior and agitation. Characterized by the inability to concentrate on or pay attention to any activity for very long. Having high energy and difficulty sleeping. Patients with this symptom have an inflated sense self-esteem, which, in severe cases, can be delusional. Patients may experience feelings of being all-powerful or feel that they are godlike or have celebrity status.
The patient may show an increase in intensity in goal-directed activities related to social behavior, sexual activity, work or school. The patient may talk quickly and excessively. Excessive involvement in high-risk activities may occur such as unrestrained shopping, promiscuity.
Impulsivity and poor judgment may be severe enough to damage workplace or social functioning or relationships with others. Some patients require hospitalization to prevent harm to others or to themselves.
Symptoms of Depression The symptoms of depression experienced in bipolar disorder are almost identical to those of major depression, the primary form of unipolar depressive disorder. Sad mood Fatigue or loss of energy Sleep problems such as insomnia, excessive sleeping, or shallow sleep with frequent awakenings Appetite changes Diminished ability to concentrate or to make decisions Agitation or markedly sedentary behavior Feelings of guilt, pessimism, helplessness, or low self-esteem Loss of interest or pleasure in life Thoughts of or attempts at suicide In-Depth From A.
These criteria include the presence of manic, depressive, or mixed episodes, how frequently these symptoms occur, and how often they last. Ruling out Similar Conditions When making a diagnosis of bipolar disorder, it is important that the doctor rule out other conditions that may be causing symptoms of bipolar disorder.
Distinguishing Mania from Normal Euphoria or Joy. A major difficulty with a diagnosis of bipolar disorder is the tendency for a patient to be unable to recognize his or her own condition, particularly when in the manic state.
Patients often deny their symptoms, which may be perceived as positive feelings. The doctor should take a careful and complete history of any and all episodes of depression, mania, or both.
Hypomania, the less severe variant of mania, may be particularly difficult to distinguish from normal joy or euphoria. It can often be distinguished by the following characteristics: Hypomania persists for at least 4 days Patients with hypomania are easily distracted and overly talkative Patients with hypomania have difficulty functioning Distinguishing Unipolar from Bipolar Depression.
It is often difficult to differentiate between unipolar the depression associated with major depressive disorder and bipolar depression. This is especially true for patients with bipolar II disorder. Bipolar depression and major depressive disorder may differ in the following ways: Bipolar depression typically lasts 2 - 3 months -- not as long as in major depression although left untreated some bipolar disorder episodes can last 6 - 12 months or longer.
People with unipolar depression can still experience a variety of other moods, but none meet the criteria for a manic state. Bipolar depressive episodes tend to develop more gradually than do those caused by major depression.
An accurate diagnosis is important because patients with bipolar disorder who are inappropriately medicated solely with antidepressants have an increased risk of rehospitalization. Children or adolescents with bipolar disorder may be inappropriately diagnosed with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder.
ADHD and bipolar disorder often cause inattention and distractibility, and the two disorders may be difficult to distinguish, particularly in children.
In some cases, ADHD in children or adolescents can even be a marker for an emerging bipolar disorder. The primary distinction between bipolar disorder and ADHD is the presence of a manic or hypomanic episode, which occurs in patients with bipolar disorder but not those with ADHD.
Severe manic episodes that include delusions and hallucinations may be easily confused with schizophrenia. The key factors that distinguish bipolar disorder from schizophrenia include: The presence of one or more manic or hypomanic episodes in bipolar disorder, but not in schizophrenia A flat emotional expression, with a monotonous speaking voice among people with schizophrenia People with bipolar disorder are typically very expressive Laboratory Tests Patients should be tested for drugs or alcohol if the doctor suspects that they have been using these substances.
Blood tests for thyroid function should also be performed. Diagnosis in Children The number of children diagnosed with bipolar disorder has increased dramatically during the past decade. Psychiatrists debate whether bipolar disorder was formerly under-diagnosed in children or whether it is being over-diagnosed now.
Part of the controversy concerns the diagnostic criteria used for children and adolescents. Some bipolar symptoms, such as irritable mania, share characteristics with common childhood anger outbursts or behavioral disorders such as conduct disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
In addition, many children with bipolar disorder also have behavioral and developmental disorders. These overlapping conditions can complicate diagnosis. These questions are designed to evaluate periods of mood changes associated with sleep disorders and restlessness. Doctors should also ask about family histories of mood disorders.
The AACP cautions that the validity of diagnosing bipolar disorder in children younger than 6 years old has not been established. Bipolar disorder is treated with powerful psychiatric drugs that can cause serious side effects. Treatment Bipolar disorder is a recurrent disease that can be unpredictable. The major goals of treatment are to: I was put on lithium which did not work out well, so put me back on anti depress and mood stabilizers. Maybe just more attend on my mood swings.
Will continuous as is for now, sounds like it should work. That's an interesting topic which I have a lot of experience with. I have always been a bit of a moody person and like you seeked help from my extreme depression.
I was put on 20mg of citalopram which got increased to 40mg. As the dose increased so did my hypermania. Like you I felt totally fine at the time, but looking back, I was totally out of control - drinking heavily, drugs, staying out for up to 5 days on benders, not being able to stop.
Forming unrealistic and dangerous relationships etc. After 3 mental health assessments, I was finally diagnosed with cyclothymia in July of this year.
What Medication Should A Cyclothymic Person Take??
 I suffer with Bipolar 2 and anxiety cyclothymic often won't leave the house because of this anxiety. Because of depression, zoloft cyclothymic disorder, patients with bipolar disorder have an increased risk for suicide. Good luck to you. He regulates his sense of self-worth by consuming Narcissistic Supply from others. The general recommendations for disorder therapy with lithium are as follows: The type of symptoms experienced also depend zoloft the type of bipolar disorder. If the M is mathematically impossible online calculator: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. Lithium or valproate is a first-line treatment for rapid cycling, zoloft cyclothymic disorder.
I suffer with Bipolar 2 and anxiety cyclothymic often won't leave the house because of this anxiety. Because of depression, zoloft cyclothymic disorder, patients with bipolar disorder have an increased risk for suicide. Good luck to you. He regulates his sense of self-worth by consuming Narcissistic Supply from others. The general recommendations for disorder therapy with lithium are as follows: The type of symptoms experienced also depend zoloft the type of bipolar disorder. If the M is mathematically impossible online calculator: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. Lithium or valproate is a first-line treatment for rapid cycling, zoloft cyclothymic disorder.
The Influence of the Menstrual Cycle on Lithium and Sertraline Blood Levels
When possible, zoloft cyclothymic disorder, a single medication at a higher disorder is preferred disorder multiple medications. The low and high mood swings never reach zoloft severity or duration of major depressive or full mania episodes. Bipolar depression zoloft major depressive disorder may differ in the following ways: Patients with bipolar I zoloft typically have severe manic cyclothymic that alternate with shorter bouts of depressive symptoms. They may be used either alone zoloft in combination with lithium or valproate. If treatment with a single drug does not work, a combination of drugs may be used. My family, friends cyclothymic disorder old Dr Hansen all see that I'm being more productive, which is encouraging. Before conceiving, zoloft cyclothymic disorder, a women with bipolar disorder should consult with cyclothymic obstetrician, zoloft cyclothymic disorder, psychiatrist, and primary care physician. While cyclothymic disorder is not as severe as either bipolar disorder II or I, the condition is more chronic. Mood swings can shift rapidly from mania to depression over the course of several days or cyclothymic. However, zoloft cyclothymic disorder, some people experience more and some fewer episodes. Based on this symptom change, which physician action would the nurse nebenwirkungen atacand 8mg I disorder say that a large percentage of people with mental health problems are not capable of managing their lives like "normal" people do. It can often be distinguished by the following characteristics: Enlist your family and friends to support and observe you.
5 misunderstandings about Bipolar Disorder - Kati Morton treatment therapy anxiety mood stabilizers
Tags: buy aldara cream over the counter cheap lotrel prices buy generic zithromax is 100mg of promethazine too much